pH Induced Switch in the Conformational Ensemble of Intrinsically Disordered Protein Prothymosin-α and Its Implications for Amyloid Fibril Formation
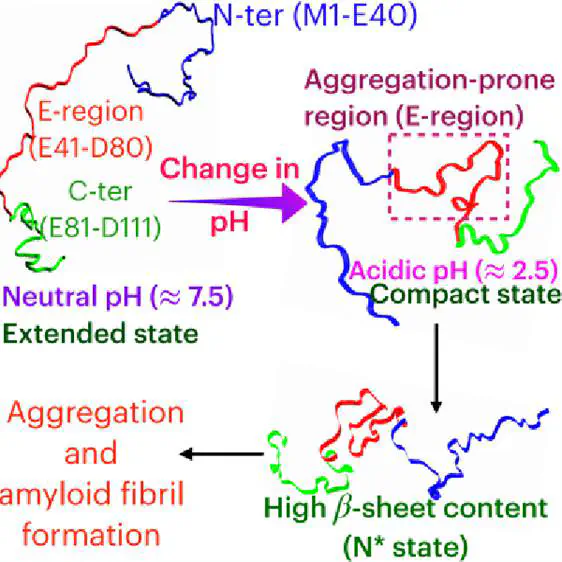 Image credit: G. Reddy
Image credit: G. Reddy
Abstract
Aggregation of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) can lead to neurodegenerative diseases. Although there is experimental evidence that acidic pH promotes IDP monomer compaction leading to aggregation, the general mechanism is unclear. We studied the pH effect on the conformational ensemble of prothymosin-α (proTα), which is involved in multiple essential functions, and probed its role in aggregation using computer simulations. We show that compaction in the proTα dimension at low pH is due to the protein’s collapse in the intermediate region (E41–D80) rich in glutamic acid residues, enhancing its β-sheet content. We observed by performing dimer simulations that the conformations with high β-sheet content could act as aggregation-prone (N*) states and nucleate the aggregation process. The simulations initiated using N* states form dimers within a microsecond time scale, whereas the non-N* states do not form dimers within this time scale. This study contributes to understanding the general principles of pH-induced IDP aggregation.